
by Jean Barbet | Jul 9, 2023 | Logic, Number Theory, Set Theory
Natural arithmetic is the science of natural numbers: it is based on addition, multiplication, natural order and divisibility. Now, all these operations and relations are defined on the basis of the single successor function, whose properties are brought together in...
by Jean Barbet | Mar 12, 2021 | Algebra, Non classé, Number Theory
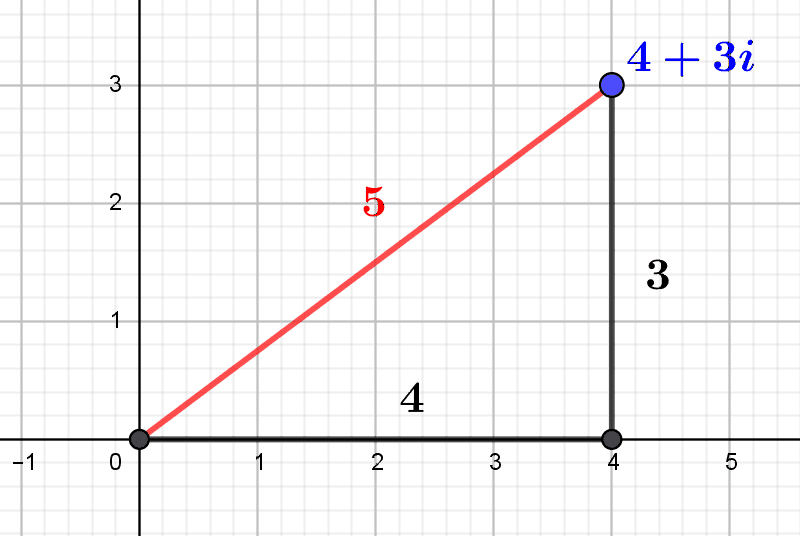
Gaussian integers are complex numbers with integer coordinates. Thanks to their norm, a kind of integer measure of their size, we can describe some of their arithmetic properties. In particular, we can determine which are the usual prime numbers that...
by Jean Barbet | Dec 16, 2020 | Non classé, Number Theory, Set Theory
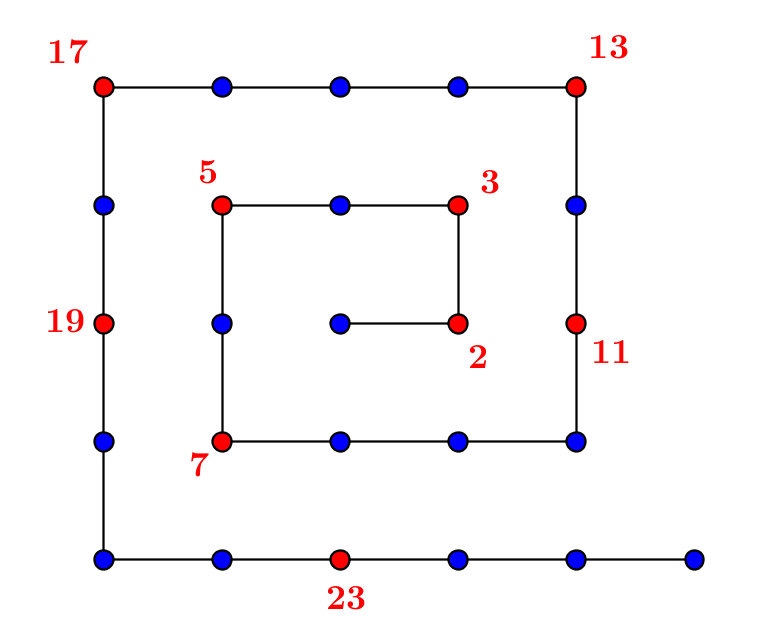
The prime natural numbers are those which have no divisors other than 1 and themselves. They exist in infinite number by Euclid’s theorem, which is not difficult to prove. 1.Prime numbers 1.1.Divisors and primes A prime number is a non-zero natural number (see...
by Jean Barbet | Nov 20, 2020 | Non classé, Number Theory, Set Theory
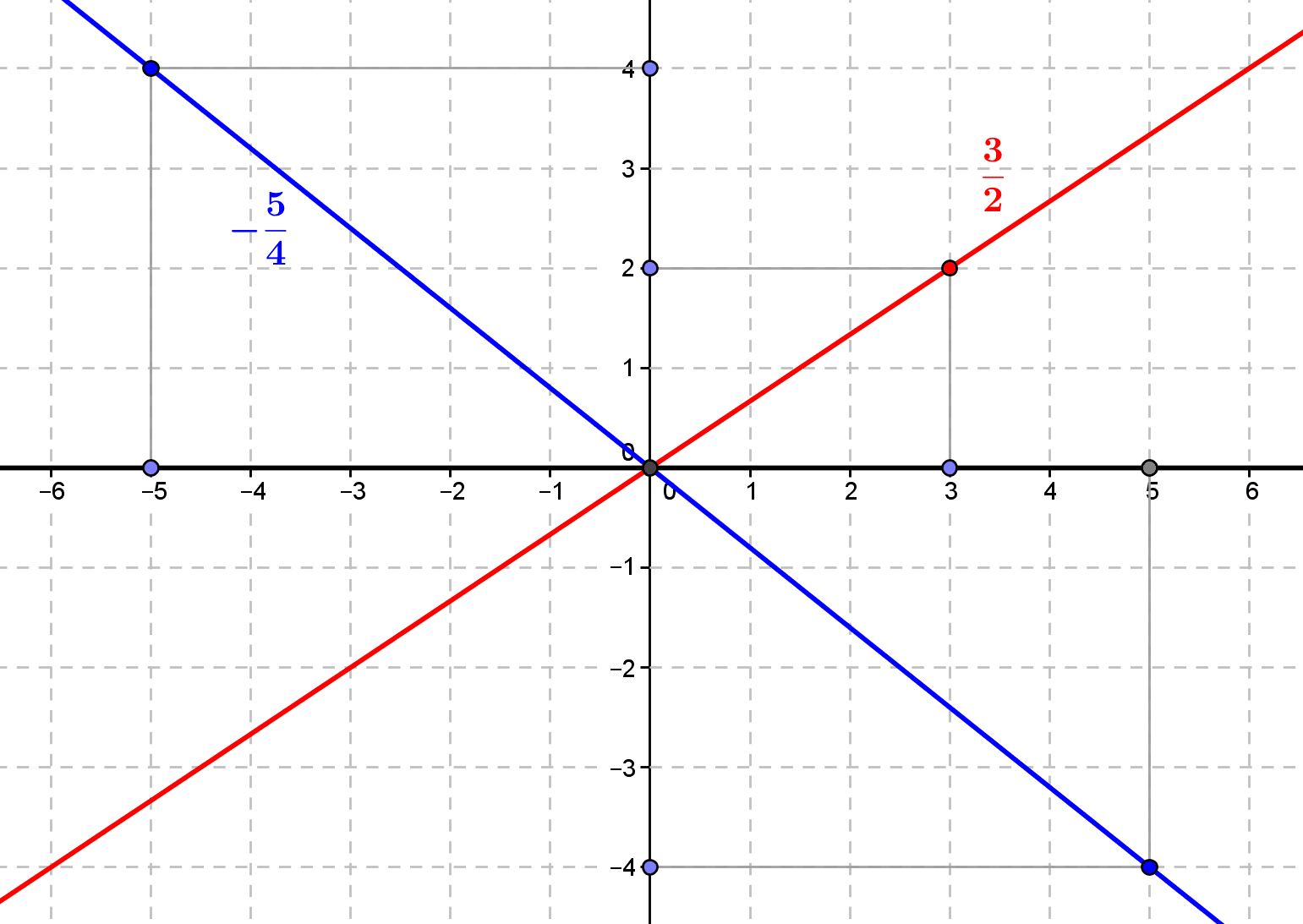
1.The intuition of rational numbers Rational numbers, i.e. “fractional” numbers, such as \(-\frac 1 2, \frac{27}{4}, \frac{312}{-6783},\ldots\), form an intuitive set which we note \(\mathbb Q\). It is an extension of the set \(\mathbb Z\) of integers (see...
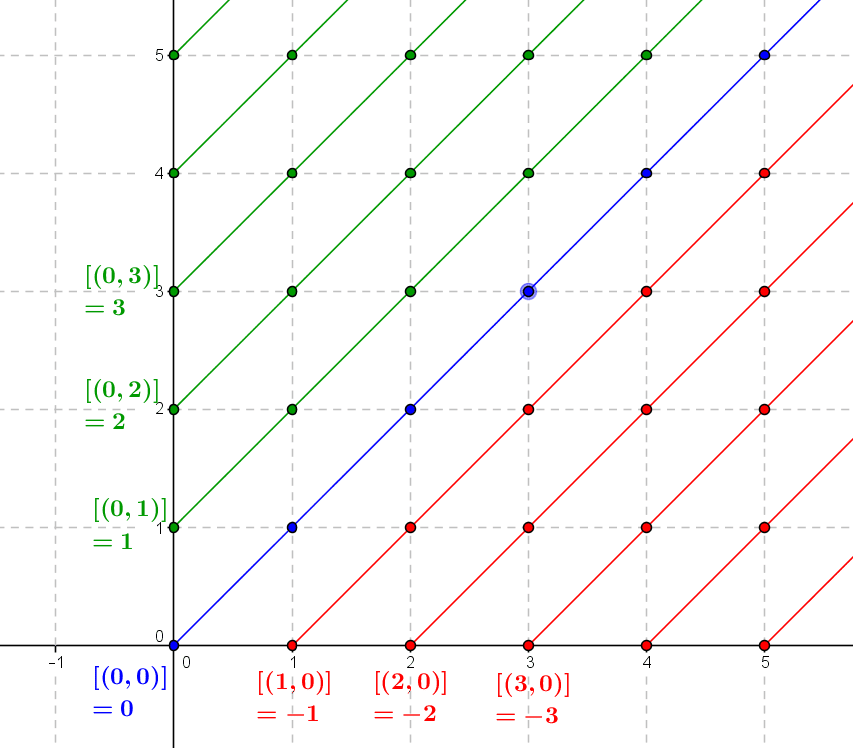
by Jean Barbet | Nov 10, 2020 | Number Theory, Set Theory
Integers are an extension of the natural numbers where the existence of subtraction provides a more appropriate framework for certain questions of arithmetic. They can be described axiomatically, but can also be constructed from the set of natural numbers and some...
by Jean Barbet | Jun 22, 2020 | Number Theory, Set Theory
Mathematical science does not seek to define the notion of a natural number, but to understand the set of natural numbers. “Natural numbers have been made by God, everything else is the work of men”. Leopold Kronecker 1.We don’t define the natural...







